Phosphoramidites
Background
BOC Sciences provides high-quality phosphoramidites to manufacturers of oligonucleotides (oroligoribonucleotides).
The phosphoramidite method is one of the strategies of nucleic acid chemical synthesis. Each cycle of the synthesis of nucleic acid chains is through high-efficiency and chemically active nucleotide 3'-phosphoramidite intermediates, which become stable pentavalent phosphate triesters after oxidation. The phosphoramidite method is currently the most commonly used DNA automated solid-phase synthesis method.
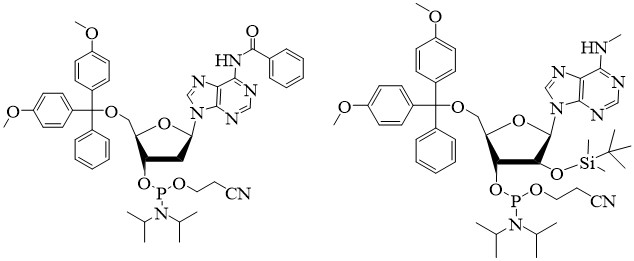
The phosphoramidite unit synthesized by DNA is mainly composed of bases, deoxyribose, 5'-DMT (4',4'-dimethoxytrityl) and 3'end 2-cyanoethyl-N, N, N ', N'-Tetraisopropyl phosphorodiamidite composition. In the phosphoramidite unit of RNA synthesis, the hydroxyl group at position 2 needs to be protected to prevent cross-reaction between 2'-hydroxyl and 3'-hydroxyl (or 5'-hydroxyl) during solid-phase synthesis. The protecting group is generally tert-butyldimethylsilyl (TBDMS). In addition, if there are primary amino groups outside the ring on adenine, cytosine, guanine and some other bases, the primary amino groups need to be protected with protecting groups.
Oligonucleotide Synthesis Steps
The phosphoramidite method completes DNA synthesis on a solid-phase carrier, and the direction of synthesis is synthesis from the 3'end to the 5'end of the primer to be synthesized.
- In the first step, trichloroacetic acid reacts with the nucleotides pre-linked to the solid phase carrier (CPG) to remove the protective group DMTr on the 5'-hydroxyl group to obtain the free 5'-hydroxyl group.
- In the second step, the phosphoramidite-protected nucleoside monomer undergoes a coupling reaction with the free 5'-hydroxyl group in the presence of an activator to obtain an intermediate whose 3'end is activated and the 5'-hydroxyl group is protected by DMTr.
- In the third step, the 5'-hydroxyl group that has not participated in the reaction is capped with a capped reagent, so that it cannot participate in the reaction further.
- The fourth step is to oxidize the phosphite with an oxidizing agent.
- By repeating the above cycle, an oligonucleotide having the desired sequence can be synthesized.
- After the synthesis is completed, the final synthesized oligonucleotide is cut from the solid phase carrier (CPG) by high temperature treatment with ammonia water for further purification to obtain the target oligonucleotide.
Resources

- Hoechst Dyes: Definition, Structure, Mechanism and Applications
- Mastering the Spectrum: A Comprehensive Guide to Cy3 and Cy5 Dyes
- Fluorescent Probes: Definition, Structure, Types and Application
- Fluorescent Dyes: Definition, Mechanism, Types and Application
- Coumarin Dyes: Definition, Structure, Benefits, Synthesis and Uses
- Unlocking the Power of Fluorescence Imaging: A Comprehensive Guide
- Cell Imaging: Definitions, Systems, Protocols, Dyes, and Applications
- Lipid Staining: Definition, Principles, Methods, Dyes, and Uses
- Flow Cytometry: Definition, Principles, Protocols, Dyes, and Uses
- Nucleic Acid Staining: Definition, Principles, Dyes, Procedures, and Uses
Online Inquiry
















