NHS Esters
Background
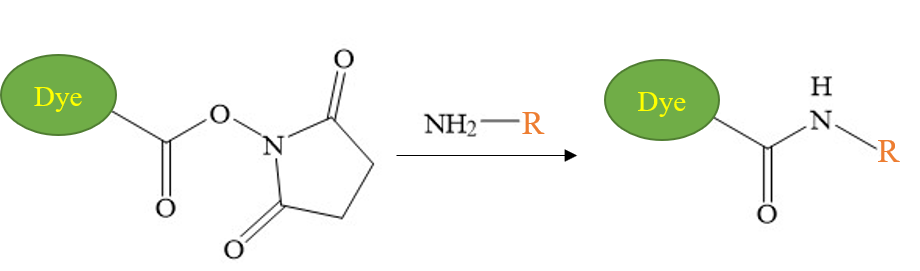
Primary or secondary amino groups are common in biomolecules such as proteins and peptides. Activated esters (such as sulfotetrafluorophenyl-STP, N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) ester, etc.) are reactive compounds suitable for modifying amino groups. NHS esters are the most commonly used amine reactive reagents.
Under physiological pH or even weakly alkaline conditions, NHS esters can react with primary amines to form very stable amide bonds. Both the N-terminal α-amino group and the lysine residue ε-amino group of the protein can form an amide bond with the NHS ester.
The amide bond formed by NHS ester and amino group is exactly the same as the peptide bond in natural protein. NHS esters are generally stable and show high reactivity and selectivity with aliphatic amines, and are very suitable for labeling and bioconjugation of biomolecules.
Reaction conditions
- Solvent
- pH
- Temperature
- Reaction buffer solution
- The amount of reaction
NHS ester can be divided into water-soluble and water-insoluble. Water-soluble NHS esters can react stably in the water phase. Water-insoluble NHS esters are mainly dissolved in polar aprotic organic solvents that are miscible with water, such as DMF or DMSO.
The reaction between NHS ester and amine strongly depends on pH, and the acylation reaction of amine is usually carried out at pH 7.5 or higher. Protein modification reactions are usually carried out at pH 7.5-8.5.
Most bioconjugation reactions of NHS esters are carried out at room temperature or 4°C.
Avoid using buffer solutions containing free amino groups. The ammonium salt must be removed before the conjugation reaction (such as commonly used protein precipitation agents such as ammonium sulfate and ammonium acetate).
The amount of NHS ester is generally 8 times the amount of protein in excess. The specific dosage also needs to be determined according to the structure, solubility, and solution concentration of the protein solution.
Resources

- Hoechst Dyes: Definition, Structure, Mechanism and Applications
- Mastering the Spectrum: A Comprehensive Guide to Cy3 and Cy5 Dyes
- Fluorescent Probes: Definition, Structure, Types and Application
- Fluorescent Dyes: Definition, Mechanism, Types and Application
- Coumarin Dyes: Definition, Structure, Benefits, Synthesis and Uses
- Unlocking the Power of Fluorescence Imaging: A Comprehensive Guide
- Cell Imaging: Definitions, Systems, Protocols, Dyes, and Applications
- Lipid Staining: Definition, Principles, Methods, Dyes, and Uses
- Flow Cytometry: Definition, Principles, Protocols, Dyes, and Uses
- Nucleic Acid Staining: Definition, Principles, Dyes, Procedures, and Uses
Online Inquiry














