Controlled Pore Glass (CPG) Solid Supports for Oligonucleotide Synthesis
-
 Alkyne CPG 1000A
Alkyne CPG 1000ACAT:
-

-

-

-

-

-
 rA-CPG
rA-CPGCAT:
-
 rC-CPG
rC-CPGCAT:
-
 rG-CPG
rG-CPGCAT:
-
-cpg-1000.gif)
-
 MGB CPG 1000
MGB CPG 1000CAT:
-
 Phosphate CPG 500 v2
Phosphate CPG 500 v2CAT:
-

-

-

-

-
-cpg.gif) GalNAc(TEG)-CPG
GalNAc(TEG)-CPGCAT:
-
 Yakima Yellow® CPG
Yakima Yellow® CPGCAT:
-

Background
BOC Sciences provides high-quality controlled pore glass (CPG) to ensure efficient and accurate synthesis of oligonucleotides.
CPG is a rigid derivatized microporous glass ball made of silica. It is compatible with any solvent and is relatively stable to corrosive solvents and high temperature and high pressure. It is now widely used as a support for solid-phase synthesis of oligonucleotides. There are many irregular holes in the CPG sphere. The size of the pore is called the pore size. The pore size of the CPG depends on the length of the synthesized oligonucleotide. Generally, when the synthetic chain length is less than 60-mer, choose a CPG with a pore size of 500 angstroms; when the synthetic chain length is greater than 60-mer, choose a CPG with a pore diameter of 1000 angstroms. The condensation efficiency of using CPG is as high as 98%-99%, which can meet the conditions for the synthesis of oligonucleotides up to 175-mer.
Application
CPG can be used as a solid support material required in the solid-phase synthesis of oligonucleotides.
In biology, DNA/RNA synthesis requires DNA/RNA polymerase and template strands. Nucleoside triphosphate (NTP) is successively added to the template chain using the principle of base complementary pairing. Catalyzed by DNA/RNA polymerase, DNA/RNA with phosphodiester bond structure is formed. This method has the problems of low sample purity and difficulty in arbitrarily designing nucleotide sequences. In response to these problems, scientists have discovered a solid-phase phosphoramidite chemistry method to synthesize short strands of DNA/RNA (i.e., oligonucleotides) without the help of DNA/RNA polymerases and templates, and completely through organic chemistry, and realized the automation and commercialization of oligonucleotide synthesis.
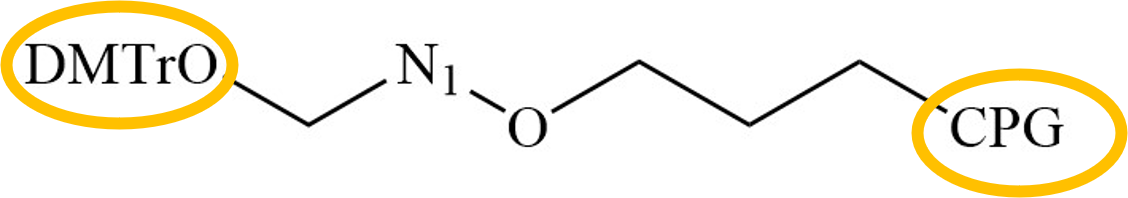
At present, the most commonly used commercial automatic synthesis methods are solid-phase synthesis, and solid-phase synthesis involves immobilizing nucleic acid on a solid-phase carrier to complete the synthesis reaction. The 3'terminal nucleoside (N1) of the oligonucleotide chain to be synthesized is coupled to the solid support through a long alkyl arm with its 3'-hydroxyl group. The 5'-hydroxyl group of the nucleotide is protected with dimethoxytrityl (DMTr). Controlled pore glass (CPG) is a commonly used solid phase carrier.
Resources

- Hoechst Dyes: Definition, Structure, Mechanism and Applications
- Mastering the Spectrum: A Comprehensive Guide to Cy3 and Cy5 Dyes
- Fluorescent Probes: Definition, Structure, Types and Application
- Fluorescent Dyes: Definition, Mechanism, Types and Application
- Coumarin Dyes: Definition, Structure, Benefits, Synthesis and Uses
- Unlocking the Power of Fluorescence Imaging: A Comprehensive Guide
- Cell Imaging: Definitions, Systems, Protocols, Dyes, and Applications
- Lipid Staining: Definition, Principles, Methods, Dyes, and Uses
- Flow Cytometry: Definition, Principles, Protocols, Dyes, and Uses
- Nucleic Acid Staining: Definition, Principles, Dyes, Procedures, and Uses
Online Inquiry

