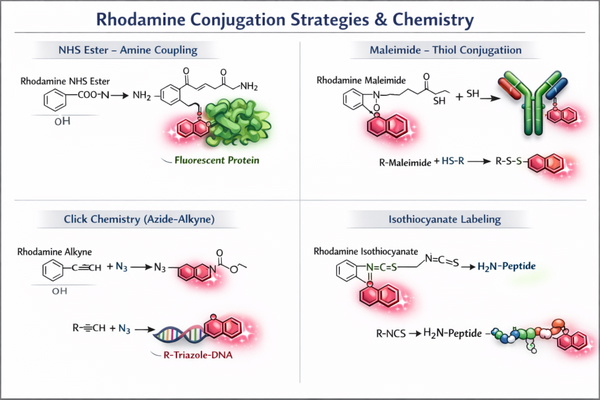
Rhodamine Labeling Strategies Designed for Your Specific Biomolecules
12-25-2025
Rhodamine labeling, as a key fluorescence labeling technique for biomolecules, has become an indispensable tool in cell imaging, protein localization, nucleic acid analysis, and molecular interaction studies due to its high brightness, excellent photostability, and broad applicability. Through customized Rhodamine labeling strategies tailored for proteins, antibodies, nucleic acids, peptides, and small-molecule probes, researchers can achieve high-sensitivity detection, precise visualization, and multichannel colocalization analysis, enabling in-depth investigation of dynamic processes and molecular mechanisms within complex biological systems.
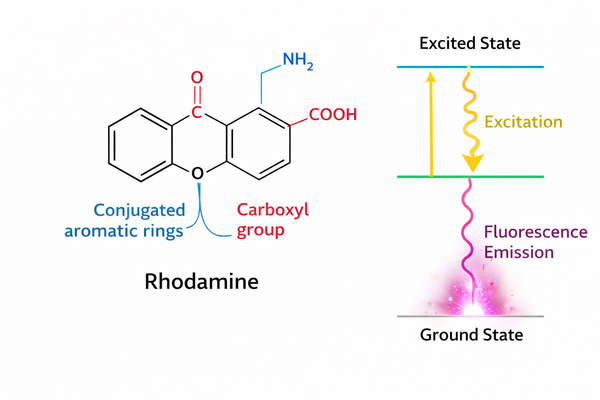
Rhodamine Spectral Properties and Fluorescence Mechanism Explained for Research Use
12-25-2025
Rhodamine dyes, as core fluorophores in bioanalytical and optical imaging applications, have become one of the most widely used fluorescent probe families in chemical biology research. This is due to their excellent molar extinction coefficients, extremely high quantum yields, and outstanding photophysical stability in complex physiological environments. These dyes are based on the rigid xanthene core structure, which effectively suppresses non-radiative energy dissipation, enabling high-brightness photon emission in the excited state. A deep understanding of rhodamine’s spectral properties and the underlying electronic transition mechanisms is critically important for researchers to precisely control experimental parameters, develop novel fluorescent sensors, and enhance the sensitivity of biomolecular detection.
Rhodamine vs Other Fluorophores: How to Choose the Best Dye?
10-31-2025
Rhodamine, one of the most representative fluorescent dyes in life science research, is highly favored for its exceptional brightness, outstanding photostability, and extensive range of derivatives. Its unique chemical structure allows versatile functional modifications, enabling efficient conjugation with proteins, nucleic acids, and small molecules. Rhodamine dyes are widely applied in cell imaging, flow cytometry, and in vivo fluorescence tracking. With the continuous advancement of fluorescence technologies, other dyes such as Fluorescein, Cyanine, Alexa Fluor, and BODIPY have also demonstrated distinct advantages in terms of performance and application. Given the wide variety of fluorescent dyes available, researchers must evaluate multiple parameters—including excitation and emission wavelengths, quantum yield, photostability, and biocompatibility—to select the most suitable dye for their experimental needs. This article provides an in-depth comparison of Rhodamine and other major fluorescent dyes, offering a scientific guide to dye selection and helping researchers achieve higher signal intensity and detection precision across diverse experimental systems.
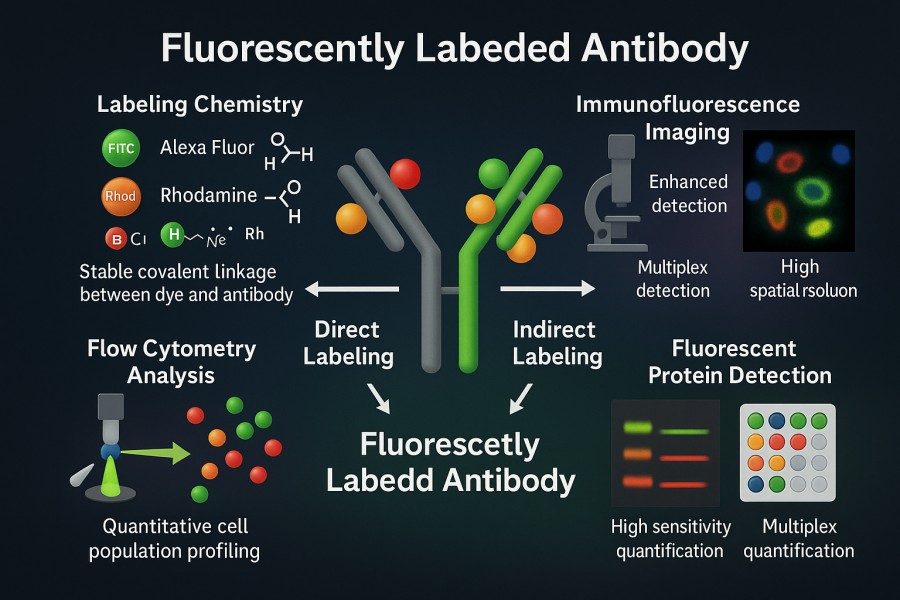
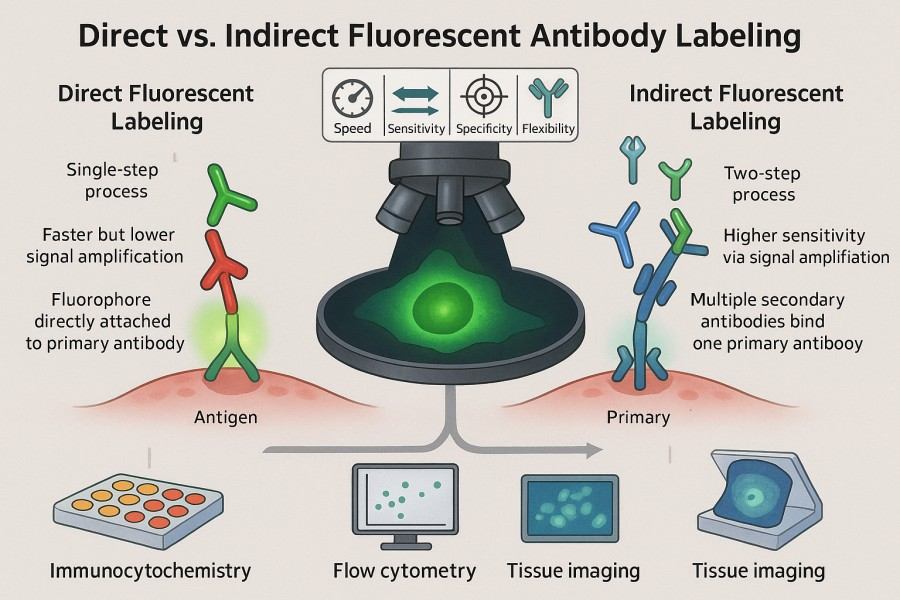
Direct vs. Indirect Fluorescent Antibody Labeling: Which Is Right for Your Research?
10-31-2025
Fluorescent labeled antibodies have become indispensable tools in modern life science research, offering high sensitivity and visualization capabilities for protein detection, cell imaging, and multiplexed analysis. Whether in basic research or clinical diagnostics, scientists rely on these labeled antibodies for accurate identification and quantification of target molecules. In experimental design, choosing between direct fluorescent antibody labeling and indirect fluorescent antibody labeling is a critical decision, as each approach presents distinct advantages and limitations in terms of sensitivity, specificity, operational complexity, and signal stability. By thoroughly understanding the principles and applications of both methods, researchers can optimize their strategies to achieve more efficient and reliable protein detection and visualization outcomes.
A Practical Guide to Fluorescent Labeling of Antibodies: Principles, Challenges, and Applications
10-31-2025
Antibody labeling, as a core technology in modern biological research and diagnostic experiments, enables highly sensitive detection and visualization of target proteins by coupling specific antibodies with fluorescent dyes. Fluorescently labeled antibodies not only reveal the spatial distribution and dynamic changes of proteins inside and outside cells but are also widely applied in flow cytometry, fluorescence microscopy imaging, Western blotting, and high-throughput screening platforms. With the advancement of multicolor labeling techniques and high-performance fluorescent dyes, researchers can analyze multiple target molecules simultaneously within a single experiment, greatly enhancing experimental efficiency and data reliability.
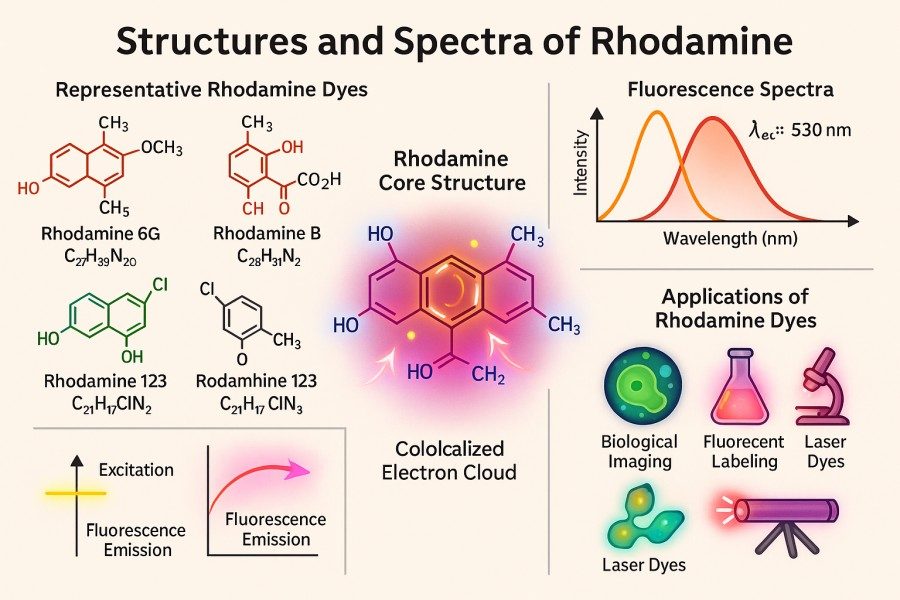
Comparing Rhodamine Derivatives: Rhodamine 6G, Rhodamine B, Rhodamine 123 and More
10-31-2025
Rhodamine dyes, as a class of classic fluorescent dyes, are widely used in fields such as bioimaging, flow cytometry, sensing probes, and materials science due to their high brightness, excellent photostability, and versatile chemical modification capabilities. With the increasing demands of modern research, scientists are paying more attention to the differences among various rhodamine derivatives in terms of spectral properties, labeling efficiency, and biocompatibility. This article systematically compares commonly used rhodamine derivatives, including Rhodamine 6G, Rhodamine B, Rhodamine 123, and other important derivatives, providing in-depth analysis on structural features, application scenarios, advantages and limitations, and experimental considerations, offering authoritative guidance and practical reference for researchers selecting and applying rhodamine dyes.
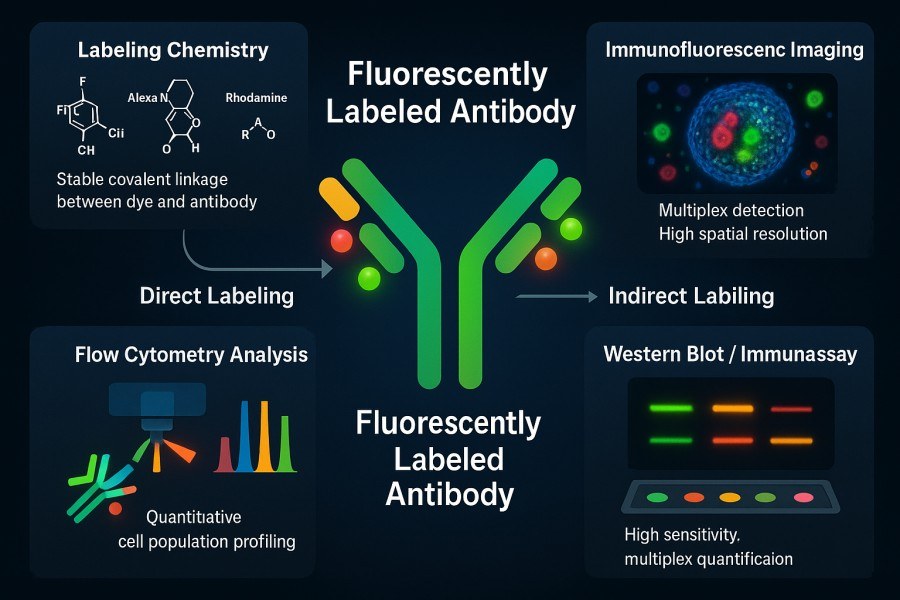
How to Select the Best Fluorophore for Reliable Antibody Labeling Results?
10-31-2025
Antibody labeling is an indispensable tool in modern life science research and diagnostic technologies. By conjugating antibodies with fluorophores, it enables highly sensitive and specific detection and visualization of target molecules. Choosing the right fluorophore not only affects signal intensity and image quality but also directly impacts the reliability of experiments and the reproducibility of data. In complex applications such as multicolor imaging, flow cytometry, or in vivo imaging, factors like excitation/emission wavelengths, photostability, brightness, and chemical compatibility of different fluorophores can significantly influence experimental outcomes. Therefore, scientifically evaluating fluorophore properties and matching them to experimental requirements is crucial for achieving high-quality antibody labeling results.
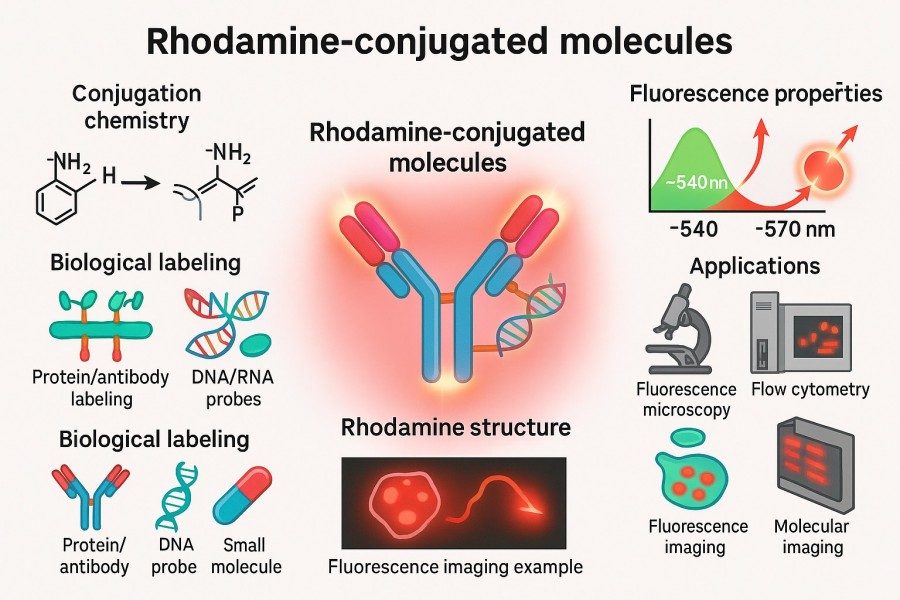
How to Optimize Rhodamine Conjugation Efficiency for Better Results?
10-07-2025
Rhodamine, as a high-brightness and stable fluorescent dye, plays a crucial role in biomolecular labeling and fluorescence imaging. However, achieving efficient Rhodamine conjugation depends not only on the quality of the dye itself but also on the choice of conjugation strategies, experimental conditions, and subsequent storage methods. This article provides an in-depth exploration of the concept, strategies, challenges, and optimization methods of Rhodamine conjugation, helping researchers achieve efficient labeling of antibodies, proteins, peptides, nucleic acids, and lipids to obtain reliable experimental results.
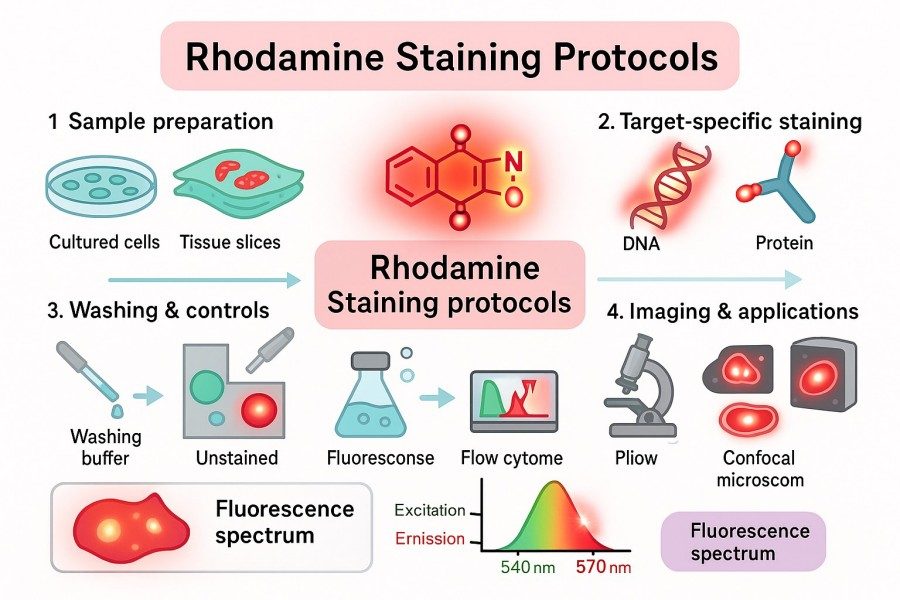
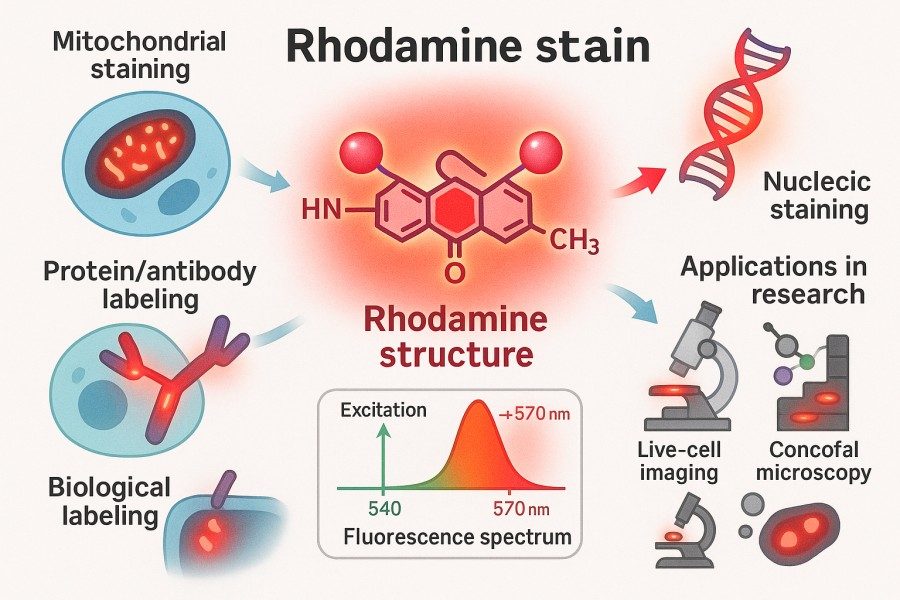
Rhodamine Staining Protocols: Tips for High-Quality and Reproducible Results
10-07-2025
Rhodamine dyes are widely used labeling tools among researchers due to their high brightness, photostability, and excellent cell permeability. Whether in cell staining, tissue section labeling, pathogen detection, or mitochondrial function studies, Rhodamine staining can provide high-resolution and reproducible imaging results. This article delves into rhodamine staining protocols from principles, types, common methods, optimization strategies, to practical applications, offering researchers practical tips to enhance staining quality and experimental reproducibility.
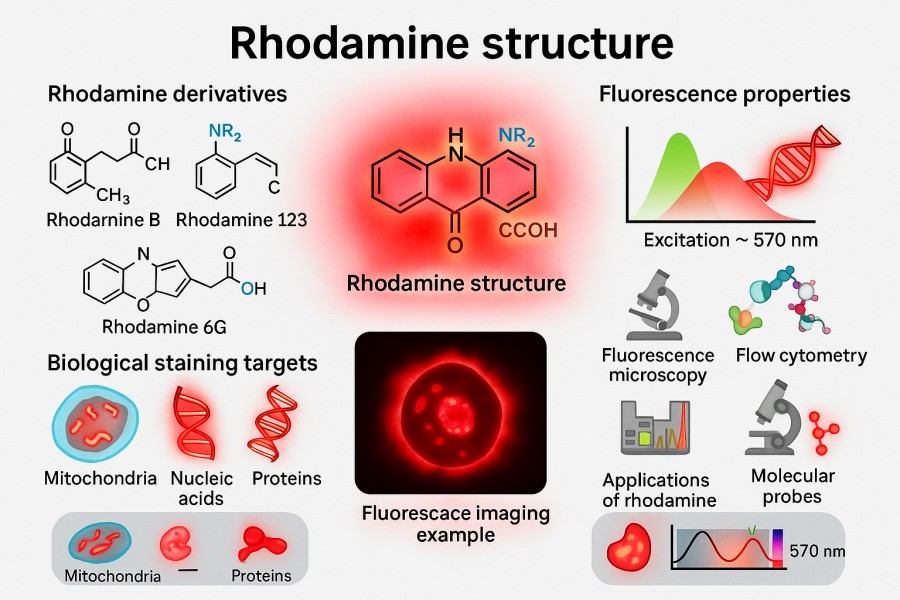
Rhodamine Synthesis: Overcoming Challenges in Fluorescent Applications
10-07-2025
Rhodamine dyes have become commonly used fluorescent reagents in scientific research and industry due to their excellent fluorescence performance, photostability, and broad applicability. In fields such as bioimaging, fluorescent probe design, and optoelectronic materials, the high brightness and tunable spectral properties of Rhodamine provide strong support for experiments. However, the synthesis of Rhodamine involves multiple chemical methods and technical routes, and the optimization of each step directly affects the dye's purity, stability, and optical properties. This article provides a comprehensive overview of Rhodamine synthesis strategies, key techniques, application directions, and best laboratory practices, aiming to offer researchers a systematic reference to achieve efficient and reproducible Rhodamine preparation and application.
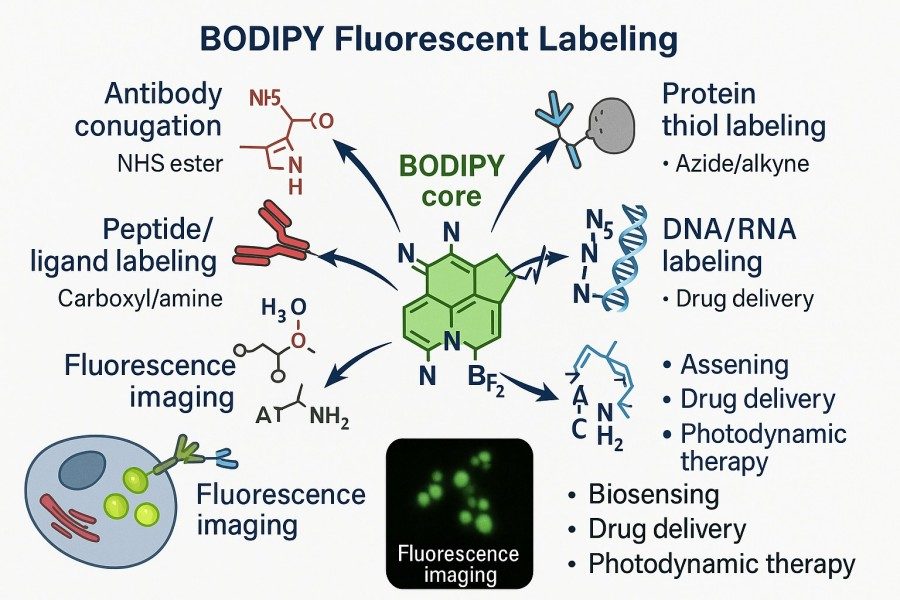
Mastering BODIPY Fluorescent Labeling: Techniques, Applications, and Expert Tips
08-29-2025
BODIPY (boron-dipyrromethene) dyes are gradually becoming the fluorescent tool of choice for researchers due to their high quantum yield, excellent photostability, narrow and tunable emission spectra, and extensive potential for molecular modification. Whether labeling proteins, peptides, lipids, or nucleic acids, BODIPY provides highly specific and bright signals, meeting the diverse needs of applications ranging from cellular imaging to high-throughput analysis. This article will explore BODIPY fluorescent labeling strategies, practical applications, and optimization tips, helping researchers overcome common challenges, enhance experimental efficiency and data reliability, and provide comprehensive technical guidance for both beginners and experienced scientists.
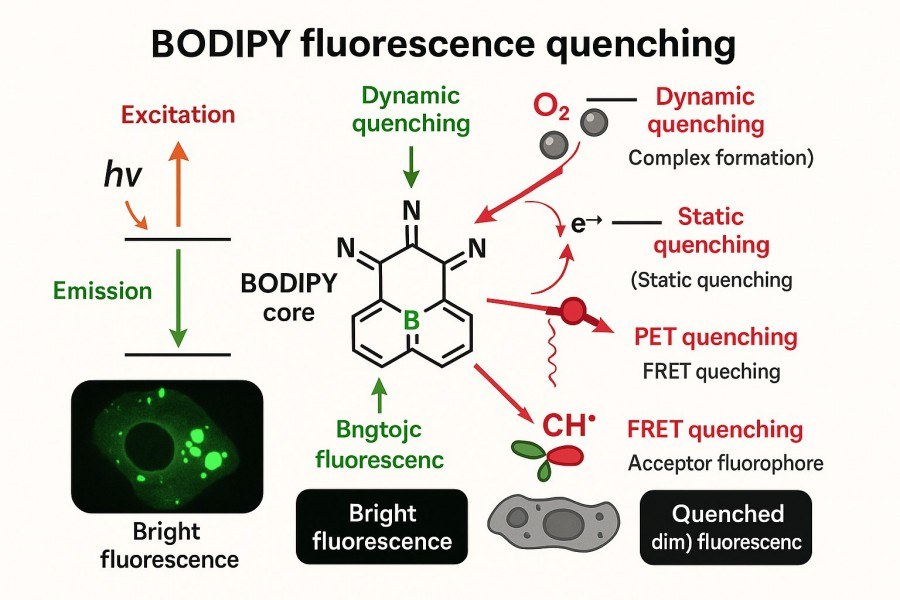
Understanding and Controlling Fluorescence Quenching in BODIPY Dyes for Optimal Probe Design
08-29-2025
BODIPY dyes, with their excellent photostability, high fluorescence quantum yields, and tunable spectral properties, have become indispensable fluorescent probes in bioimaging, optical sensing, and phototherapy research. However, in practical applications, fluorescence quenching is a critical factor that can affect BODIPY performance. Quenching not only reduces signal intensity but may also compromise probe selectivity and stability. Therefore, understanding quenching mechanisms, modulating structural factors, and implementing rational strategies are essential for developing high-performance BODIPY probes.
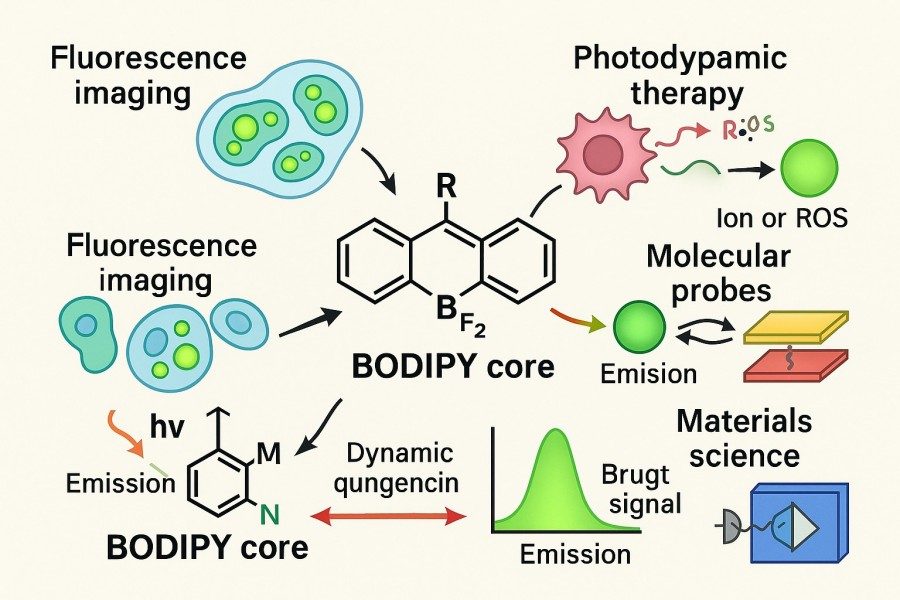
How to Modulate Photophysical, Photochemical, and Stability Properties of BODIPY Dyes?
08-29-2025
BODIPY dyes have become essential tools in fields such as bioimaging, photodynamic therapy, sensor development, and materials science due to their excellent photophysical properties, high fluorescence quantum yields, and chemical modifiability. However, native BODIPY suffers from certain limitations in emission wavelength, Stokes shift, photostability, and photochemical activity, making it challenging to meet the diverse requirements of different applications. To achieve precise utilization of high-performance BODIPY dyes, researchers need to systematically optimize their photophysical properties, photochemical behavior, and chemical/photostability through molecular structural modification and environmental tuning.
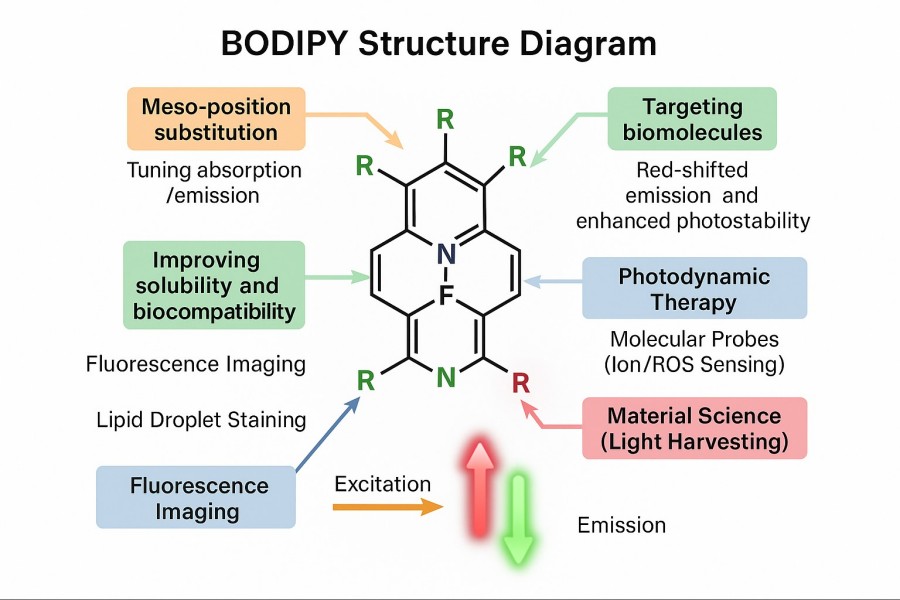
How Structural Modification of BODIPY Dyes Enhances Their Performance and Applicability?
08-29-2025
BODIPY dyes have gained widespread use in fluorescent probes, live-cell imaging, and optoelectronic materials due to their excellent photostability, sharp absorption and emission peaks, and high fluorescence quantum yield. However, native BODIPY molecules still have limitations in solubility, biocompatibility, spectral coverage, and targeting functionality. To meet the demands of complex experiments and advanced applications, scientists have systematically optimized BODIPY through structural modifications. Strategies such as core substitution, introduction of hydrophilic groups, bioconjugation, and smart responsive design not only enhance the optical performance and stability of the dyes but also enable advanced applications such as targeted delivery, functional imaging, and phototherapy. This article provides a comprehensive analysis of BODIPY structural modification methods and their value in scientific and industrial applications, helping researchers understand how customized design can improve dye performance and address common technical challenges in experiments.
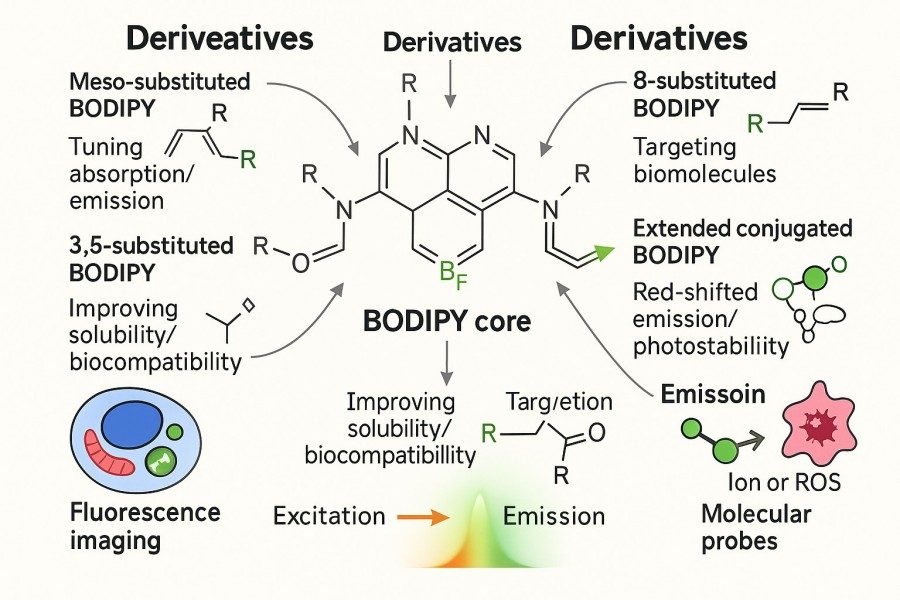
Understanding the Excitation and Emission Properties of BODIPY Dyes: A Guide for Optimal Fluorescent Probe Selection
08-29-2025
BODIPY (Boron-Dipyrromethene) dyes have become one of the most sought-after fluorescent tools for researchers due to their high fluorescence quantum yields, excellent photostability, and tunable spectral properties. However, different BODIPY derivatives exhibit significant variations in excitation and emission characteristics, and improper selection may result in weak signals, spectral crosstalk, or experimental failure. Therefore, a thorough understanding of BODIPY's optical principles, excitation/emission profiles, and structure–function relationships is essential for efficient experimental design and fluorescent probe optimization. This guide systematically explores the core structure, spectral properties, structural modification effects, and application-matching strategies of BODIPY dyes, helping researchers select the most suitable fluorescent probes for life sciences, materials science, and energy research.
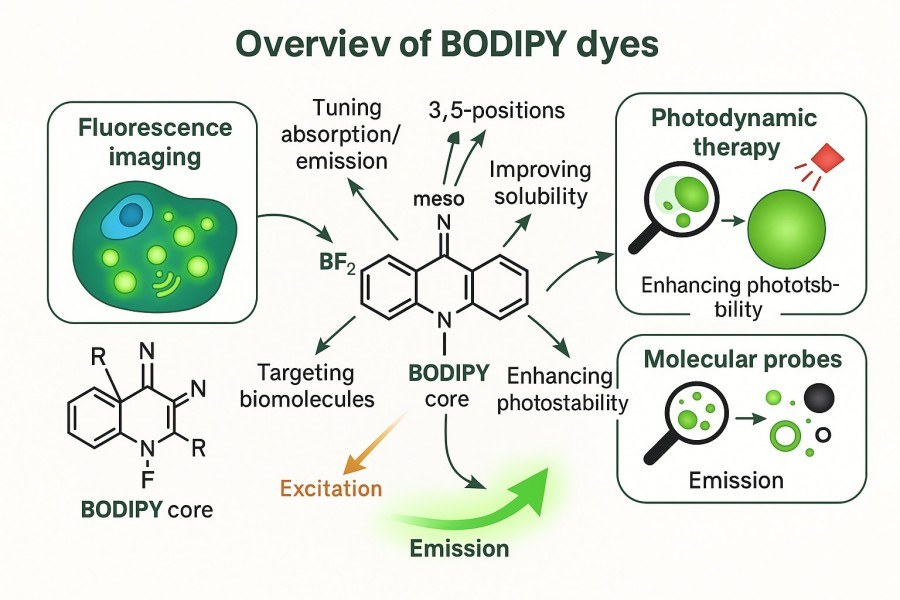
BODIPY Design, Synthesis and Functionalization: High-Performance BODIPY Derivatives
08-29-2025
In modern biochemistry and molecular imaging research, BODIPY (boron-dipyrromethene) dyes have become researchers' preferred fluorescent tools due to their excellent photophysical properties, chemical stability, and versatile derivatization potential. However, the design, synthesis, and functionalization of BODIPY dyes still face many challenges, including yield optimization, solubility control, and specific biomarking. This article provides a comprehensive analysis of BODIPY dyes—from the fundamentals, synthesis mechanisms, derivative development, and modification strategies to practical applications—highlighting their critical role in research and offering practical solutions for scientists.
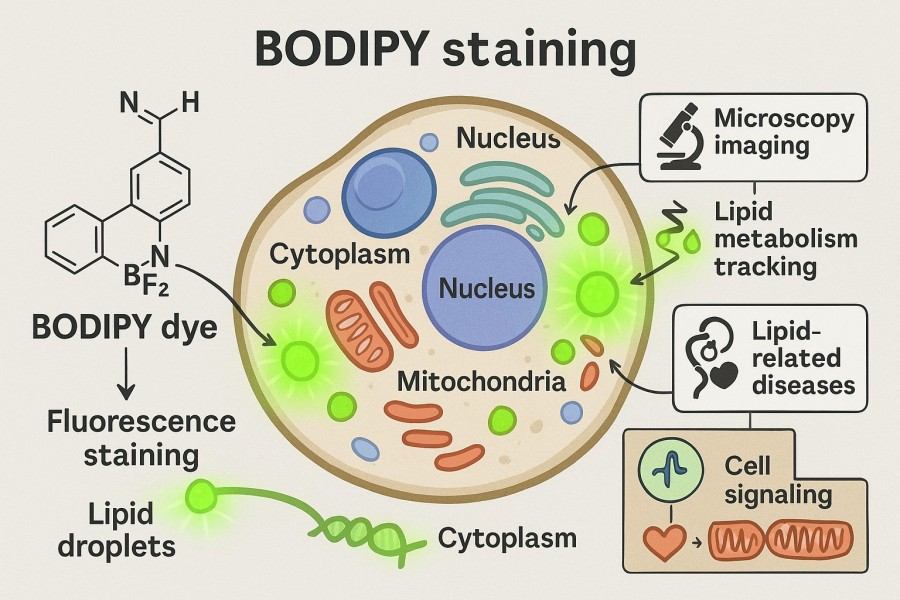
Complete Guide to BODIPY Staining for Reliable Research: Principle and Protocol
08-29-2025
BODIPY staining is a widely applied fluorescent labeling method in cell and tissue research, highly valued by researchers for its high sensitivity and stable signal. With the unique chemical structure and excellent optical properties of BODIPY dyes, scientists can directly visualize lipid droplet distribution, organelle function, and molecular dynamics. This technique not only plays an important role in fundamental cell biology and metabolic mechanism studies but is also extensively used in drug screening, disease model construction, and live-cell imaging. To achieve reliable experimental results, researchers need a deep understanding of the bodipy staining principle, master the bodipy staining protocol under different experimental systems, and flexibly optimize conditions based on sample characteristics.
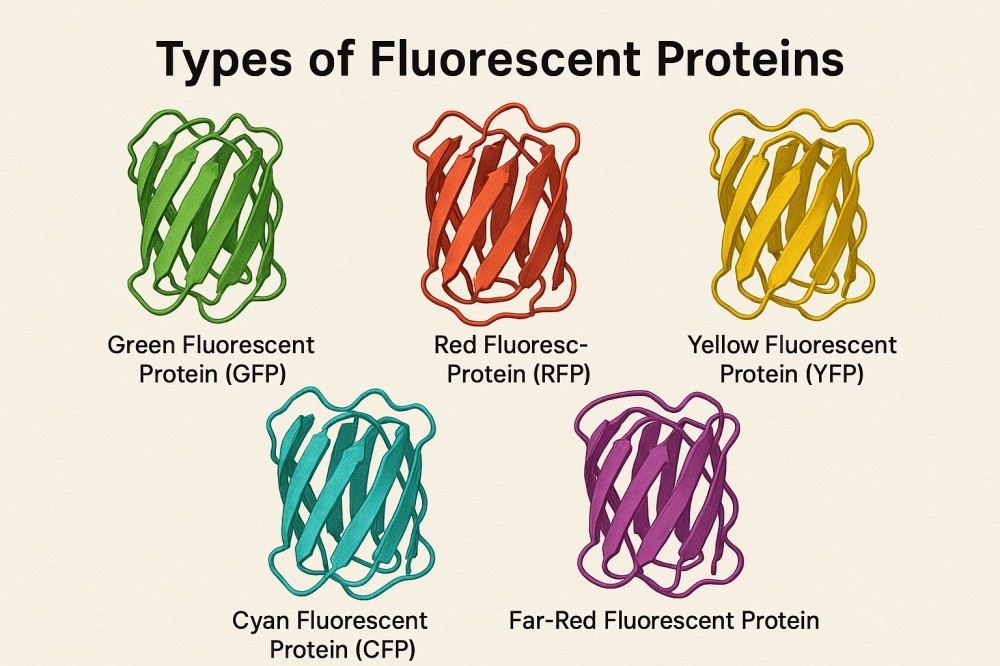
Comprehensive Guide to Fluorescent Proteins and Their Uses in Research
07-14-2025
Fluorescent proteins have their own optical characteristics and are often used as versatile fluorescent labeling tools in the life science research fields of cell imaging, protein tracking, and molecular detection. By using fluorescent proteins of different colors and spectral properties, complex multiplex labeling and dynamic monitoring can be achieved, greatly improving the sensitivity and accuracy of experiments. Structural, performance, and application studies of fluorescent proteins provide researchers with a reference to help them choose the right fluorescent protein, optimize experimental conditions, and promote the application of novel research.
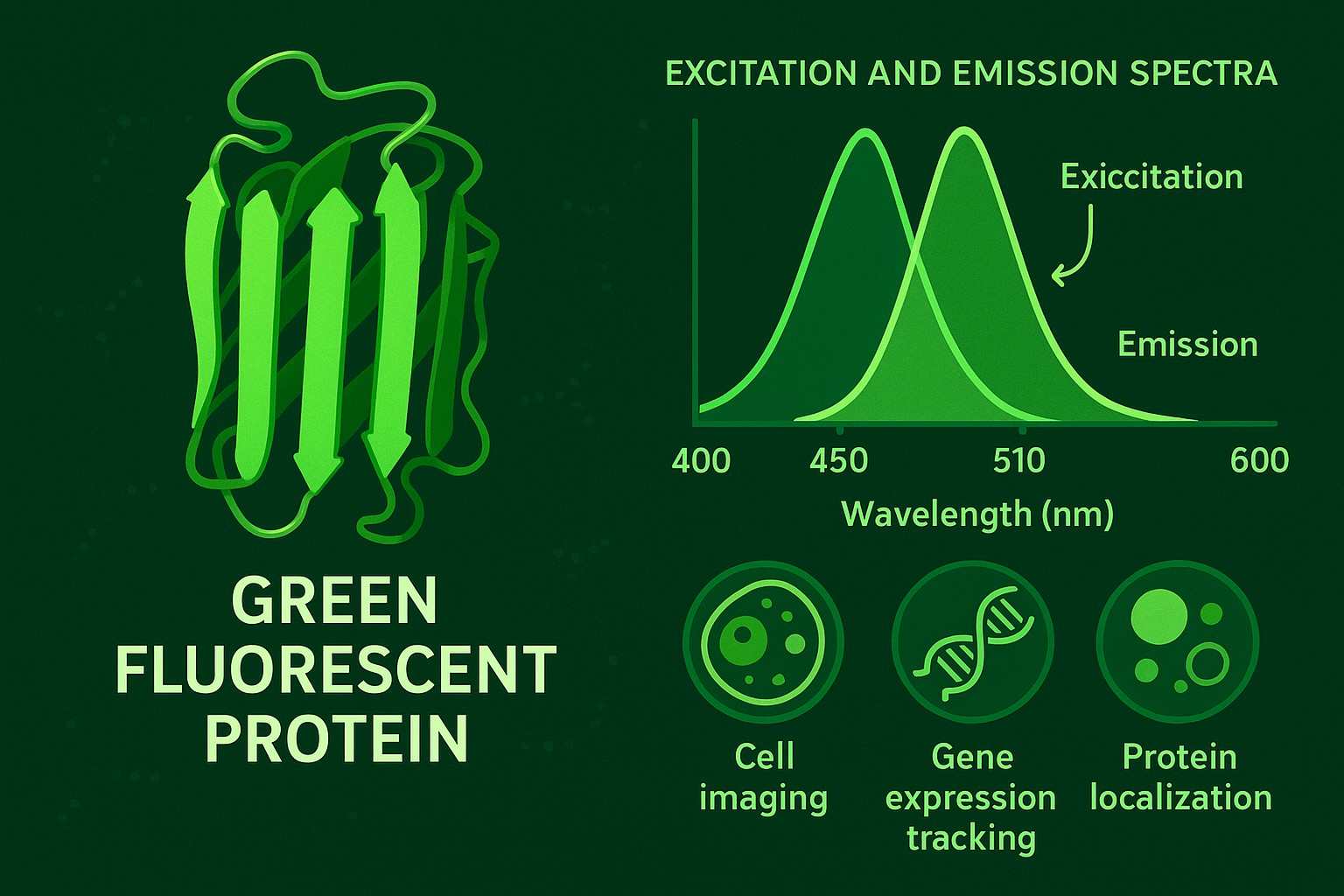
Green Fluorescent Protein: A Comprehensive Overview from Discovery to Application
07-14-2025
Green fluorescent protein (GFP), a naturally fluorescent protein from jellyfish, has been used for years to allow real-time, visual tracking of proteins and cellular imaging without interfering with the normal functions of a cell. The structure of GFP has undergone over a decade of development and optimization, leading to the creation and refinement of numerous mutants with significantly enhanced brightness, photostability, and spectral properties. GFPs and their derivatives are now used across molecular biology, cell biology, neuroscience, and drug discovery in areas such as the study of gene expression, protein localization, and cellular dynamics, and bioimaging.
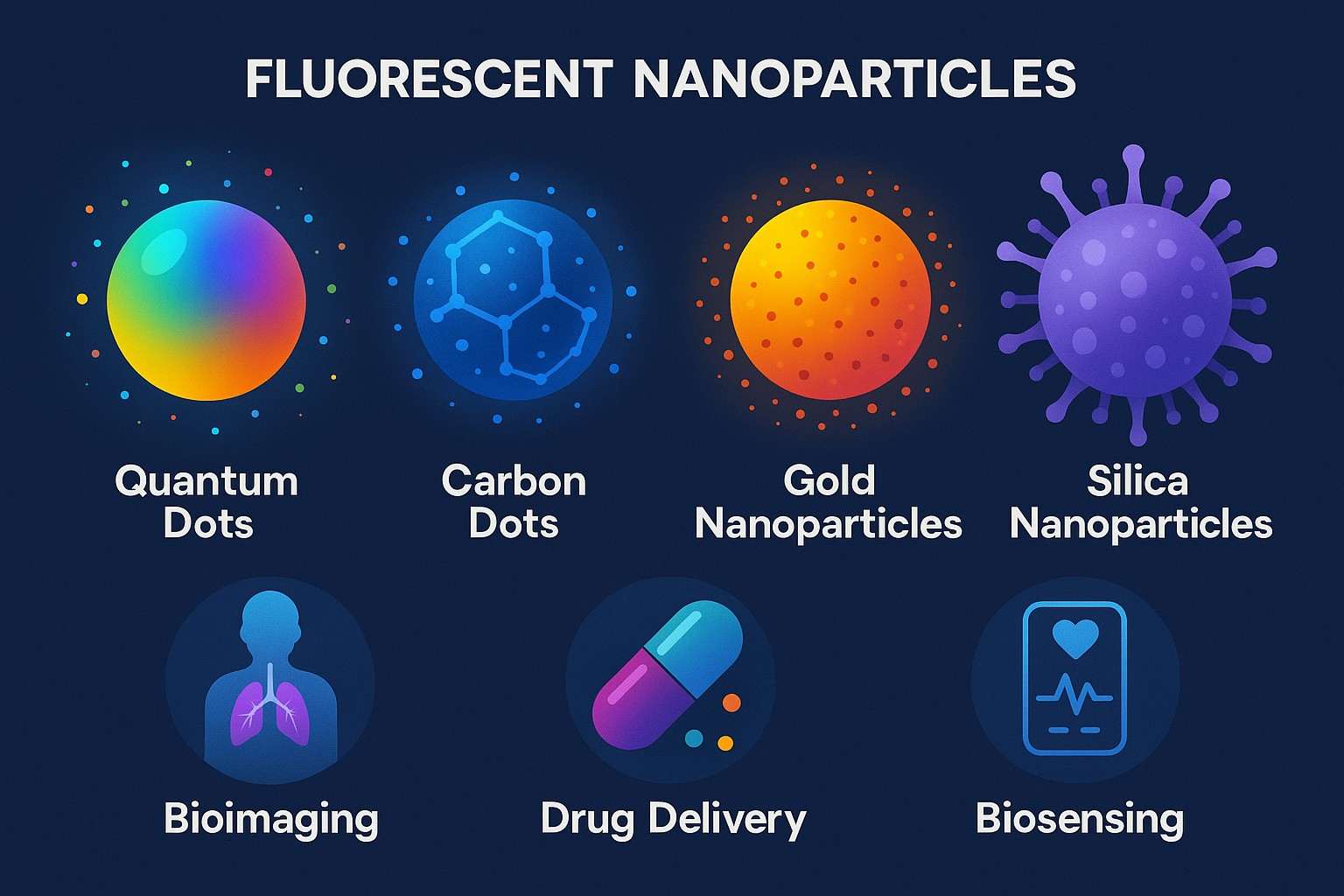
Overview of Fluorescent Nanoparticles: Applications, Challenges and Solutions
07-14-2025
Functional nanomaterials called fluorescent nanoparticles are particularly interesting for applications in bioimaging, disease diagnostics, drug delivery, and environmental sensing. Owing to their excellent optical characteristics, tunable sizes and shapes, and facile surface modification strategies, these fluorescent nanomaterials have shown great promise in biological fields as compared to conventional fluorescent dyes and proteins. They are important for conducting research and achieving success in the field of nanobiotechnology.

Mastering the Spectrum: A Comprehensive Guide to Cy3 and Cy5 Dyes
01-30-2025
In biomedical research fluorescent dyes serve as essential tools. During cell imaging and molecular biology experiments, scientists use fluorescent dyes to visualize biomolecules and cellular structures. Among many fluorescent dyes, Cy3 and Cy5 dyes distinguish themselves from other fluorescent dyes because of their distinctive spectral properties and extensive usage across various applications. The two dyes find extensive application across biological imaging and multiple scientific fields like molecular biology, proteomics, and genomics research.

Hoechst Dyes: Definition, Structure, Mechanism and Applications
01-30-2025
Fluorescent dyes are essential tools for biomedical researchers. Scientists can study living cells better through fluorescent dyes, which help them find new life science solutions quickly. From cell cycle analysis and apoptosis detection to live cell imaging, fluorescent dyes have a wide range of applications. Among all fluorescent dyes, Hoechst dyes stand apart from other fluorescent dyes because of their special features and extensive usage areas.

Fluorescent Probes: Definition, Structure, Types and Application
10-16-2024
The organism contains a multitude of chemical substances, including enzymes, proteins, and various cations and anions, which are of significant importance to human life activities and health. Additionally, there are numerous substances in nature that await testing, including antibiotics, disease markers, and pollutants, which merit further exploration by researchers. Conducting tests on these substances has positive implications, and various methods have been developed to detect specific analytes, such as chromatography, mass spectrometry, and biological methods. Each of these methods has its characteristics but tends to be time-consuming and more costly, and they cannot provide real-time information feedback.

Fluorescent Dyes: Definition, Mechanism, Types and Application
10-16-2024
Fluorescent dyes are a class of high-performance luminescent materials based on organic molecules, widely recognized for their excellent optical properties and broad application prospects. Among the various types of fluorescent dyes, rhodamine and fluorescein are the two most widely used, with extensive literature investigating their properties and applications. Other common fluorescent dyes include coumarins, polycyclic aromatic compounds, NBD-amines, naphthalimides, BODIPY dyes, cyanines, as well as thiazines and oxazines. These dyes typically exhibit good photostability, significant fluorescence intensity, and adjustable emission wavelengths, allowing them to play crucial roles in various fields such as biological imaging, optical sensing, laser technology, and display technology.

Coumarin Dyes: Definition, Structure, Benefits, Synthesis and Uses
10-16-2024
Coumarin dyes are a significant class of synthetic organic compounds derived from coumarin, known for their unique fluorescent properties and vibrant colors. These dyes are characterized by their benzopyranone structure, which contributes to their photophysical behavior, making them ideal for a wide range of applications in fields such as bioimaging, laser technology, and organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs). As research progresses, coumarin dyes continue to evolve, leading to the development of novel derivatives with tailored functionalities for specific uses in the life sciences and materials science.

BODIPY Dyes: Definition, Structure, Synthesis and Uses
10-16-2024
BODIPY dyes (boron-dipyrromethene) are a class of fluorescent compounds known for their exceptional photophysical properties, including high fluorescence quantum yields, photostability, and tunable emission spectra. These dyes have gained significant attention in various scientific and industrial fields due to their versatility. With a well-defined structure based on a boron-fluorine complex and dipyrromethene backbone, BODIPY dyes can be easily modified for specific applications. Their uses span from bioimaging and chemical sensing to photodynamic therapy and organic electronics.

Cyanine Dyes: Definition, Structure, Types and Uses
10-16-2024
Cyanine dyes are a class of synthetic dyes widely used in scientific research and industrial applications due to their unique optical properties, including strong fluorescence and tunable absorption/emission wavelengths. These dyes are particularly valued in fields such as molecular imaging, biotechnology, and materials science for their ability to label biomolecules, enhance imaging techniques, and serve as fluorescent probes. The versatile structure of cyanine dyes allows for modifications that optimize their solubility, photostability, and specificity, making them essential tools in fluorescence-based assays, medical diagnostics, and therapeutic applications.

Rhodamine Dyes: Definition, Structure, Uses, Excitation and Emission
10-07-2024
Rhodamine is an important class of flavonoid dyes. Due to its extended π-conjugated system, its open form exhibits strong fluorescence. They are used as laser dyes and in studies for detecting polymer and oligonucleotide adsorption. Dendritic polymers containing rhodamine as one of their components may have potential applications in materials science. Rhodamine dyes are used as fluorescent labeling reagents in biology because of their excellent optical properties, such as high fluorescence quantum yield, long excitation wavelength, and high photostability.

Fluorescein Dyes: Definition, Structure, Synthesis and Uses
10-07-2024
Fluorescein, a synthetic organic compound, has become an indispensable tool in biological research due to its fluorescent properties. Its bright green fluorescence under ultraviolet or blue light makes it ideal for various labeling applications in cell biology, molecular biology, and immunology. The versatility of fluorescein and its derivatives, particularly fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC), allows for the specific labeling of cells, proteins, antibodies, and nucleic acids, providing crucial insights into the structure and function of biological systems.

