Hydrazides
Background
BOC Sciences is committed to providing customers with high-quality hydrazide reactive dyes.
Hydrazide reactive dyes are carbonyl reactive dyes that can react with aldehyde groups and ketone groups in biomolecules.
Hydrazide reacts with carbonyl compounds such as aldehydes and ketones to form stable hydrazones, which is an important type of reaction. Acylhydrazone belongs to Schiff base, with stable structure, not easy to be hydrolyzed, and exhibits many superior properties. Most acylhydrazone compounds have a wide range of biological and pharmacological activities, as well as other important applications in catalysis, analysis, and photoelectricity.
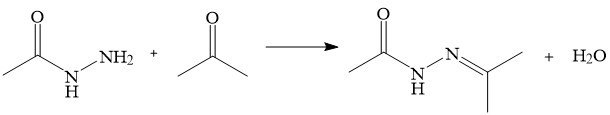 Reaction of hydrazide with carbonyl compounds
Reaction of hydrazide with carbonyl compounds
There are many ways to produce carbonyl groups in biomolecules. Specific examples are as follows:
The gradual oxidation process of biomolecules will produce active intermediate products-carbonyl complexes (biomolecules containing aldehydes and ketones). Oxygen-sensitive proteins can spontaneously form carbonyl groups when they undergo oxidative stress or deamination.
Glycoprotein is a type of sugar-containing binding protein with a wide range of functions. Glycoprotein is not only an important component of the cell membrane, intercellular matrix, plasma, mucus, hormones, etc., but also acts as a lubricant, inhibits the hydrolysis of proteolytic enzymes, and prevents bacteria and viruses from invading organisms. Periodic acid is an oxidant, which can oxidize the dihydroxy or trihydroxy in the polysaccharide residue to the corresponding aldehyde. Therefore, hydrazide reactive dyes can label glycoproteins and are suitable for the analysis of unknown samples and the identification of sample purity. This method is particularly suitable for labeling antibodies.
Oligonucleotides usually have carbonyl groups. Aldehyde pyrimidines are pyrimidine-modified bases present in a type of nucleotides. An aldehyde group is an important group for the modification of natural nucleotides in DNA.
The hydrazide reactive dyes react smoothly and almost quantitatively with various carbonyl groups in biomolecules, and can be used to label proteins, peptides, and oligonucleotides/DNA.
Resources

- Hoechst Dyes: Definition, Structure, Mechanism and Applications
- Mastering the Spectrum: A Comprehensive Guide to Cy3 and Cy5 Dyes
- Fluorescent Probes: Definition, Structure, Types and Application
- Fluorescent Dyes: Definition, Mechanism, Types and Application
- Coumarin Dyes: Definition, Structure, Benefits, Synthesis and Uses
- Unlocking the Power of Fluorescence Imaging: A Comprehensive Guide
- Cell Imaging: Definitions, Systems, Protocols, Dyes, and Applications
- Lipid Staining: Definition, Principles, Methods, Dyes, and Uses
- Flow Cytometry: Definition, Principles, Protocols, Dyes, and Uses
- Nucleic Acid Staining: Definition, Principles, Dyes, Procedures, and Uses
Online Inquiry









