Hydroxycoumarin Dyes
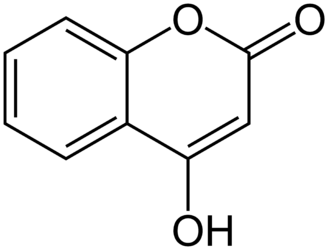
4-hydroxycoumarin
4-hydroxycoumarin is a coumarin derivative having a hydroxyl group at the 4-position. 4-hydroxycoumarin is an important fungal metabolite of coumarin precursors, and its production leads to the further fermentation of the natural anticoagulant biscoumarin. This occurs in the presence of naturally-occurring formaldehyde, which allows the second 4-hydroxycoumarin molecule to be linked to the 3-position of the first 4-hydroxycoumarin molecule through the carbon of the formaldehyde, thereby making the didimer Become a drug class. Dicoumarol appears as a fermentation product in rotten sweet clover silage and is considered a mycotoxin. 4-hydroxycoumarin is biosynthesized from malonyl-CoA and 2-hydroxybenzoyl-CoA through the enzyme 4-hydroxycoumarin synthase.
Anticoagulant
After determining biscoumarin and its anticoagulant activity, it became the prototype of a class of drugs. 4-hydroxycoumarin forms the core of the anticoagulant chemical structure and is collectively referred to as 4-hydroxycoumarin. They include, for example, warfarin (a drug used to prevent blood clots) and brodecomb (a widely used rodenticide).
7-hydroxycoumarin
7-hydroxycoumarin is a natural product of the coumarin family. It can strongly absorb ultraviolet light at several wavelengths. Despite some signs that this chemical is photomutagenic, it is in use of sunscreen. It is reported that 7-hydroxycoumarin has antioxidant properties. It is a yellow-white crystalline solid with very little solubility in hot water, but high solubility in ethanol.
 Figure 2. Chemical structure of 7-hydroxycoumarin.
Figure 2. Chemical structure of 7-hydroxycoumarin.
Synthesis
7-hydroxycoumarin is a phenylpropane, so it is synthesized from L-phenylalanine, which in turn is produced by the oxalate pathway. Phenylalanine is lyased to cinnamic acid, followed by hydroxylation from cinnamic acid 4-hydroxylase to give 4-coumaric acid. Hydroxylated 4-coumaric acid with cinnamate / coumarate 2-hydroxylase again to obtain 2,4-dihydroxy-cinnamic acid (umbellate), and then rotate the unsaturated bond adjacent to the carboxylic acid group. Finally, an intramolecular attack from the hydroxyl group of C2 'to a carboxylic acid group closes the ring and forms a lactone 7-hydroxycoumarin.
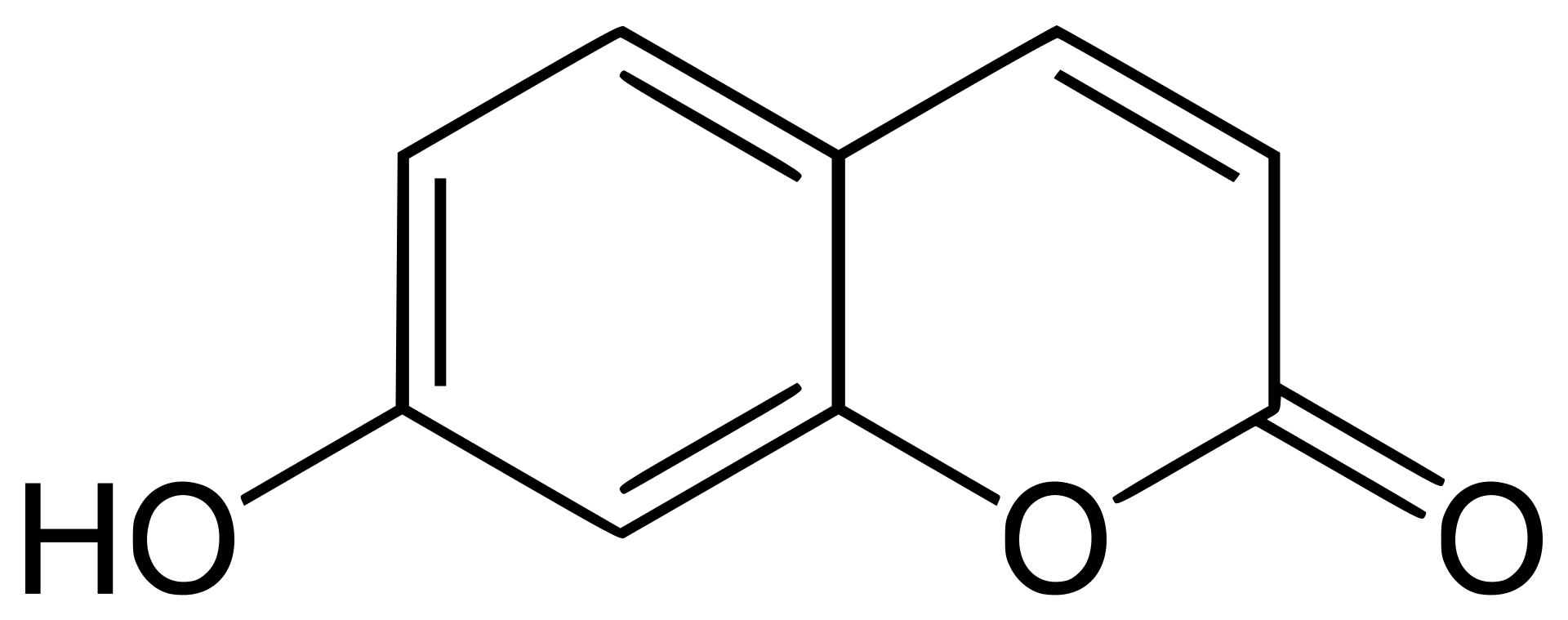 Figure 3. Synthesis of 7-hydroxycoumarin.
Figure 3. Synthesis of 7-hydroxycoumarin.
Fluorescence
7-hydroxycoumarins have strong absorption at 300, 305, and 325 nm, logε values of 3.9, 3.95, and 4.15, respectively, and emit blue fluorescence under both ultraviolet and visible light. The strong absorption of 7-hydroxycoumarins at three different wavelengths and the fact that energy is safely lost as visible light makes 7-hydroxycoumarins a useful sunscreen. Absorption in altered alkaline solution due to deprotonation of phenolic hydroxyl groups.
References:
- Du, Lupei.; et al. Rational design of a fluorescent hydrogen peroxide probe based on the umbelliferone fluorophore. Tetrahedron Letters. 2008, 49 (19): 3045–3048.
- Bye, A.; et al. The biosynthesis of 4-hydroxycoumarin and dicoumarol by Aspergillus fumigatus Fresenius. Biochemical Journal. 1970, 117 (2): 237–245.
Resources

- Hoechst Dyes: Definition, Structure, Mechanism and Applications
- Mastering the Spectrum: A Comprehensive Guide to Cy3 and Cy5 Dyes
- Fluorescent Probes: Definition, Structure, Types and Application
- Fluorescent Dyes: Definition, Mechanism, Types and Application
- Coumarin Dyes: Definition, Structure, Benefits, Synthesis and Uses
- Unlocking the Power of Fluorescence Imaging: A Comprehensive Guide
- Cell Imaging: Definitions, Systems, Protocols, Dyes, and Applications
- Lipid Staining: Definition, Principles, Methods, Dyes, and Uses
- Flow Cytometry: Definition, Principles, Protocols, Dyes, and Uses
- Nucleic Acid Staining: Definition, Principles, Dyes, Procedures, and Uses
Online Inquiry

