Acridine Yellow Dyes
Acridine yellow, also known as acridine yellow G, acridine yellow H107, basic yellow K, and 3,6-diamino-2,7-dimethylacridine, is a yellow dye with strong bluish-green fluorescence. It is a derivate of acridine. In histology, it is used as a fluorescent stain, and as a fluorescent probe for non-invasive measurements of cytoplasmic pH changes in whole cells. It is also used as a topical antiseptic. It is usually available as a hydrochloride salt. Acridine yellow damages DNA and is used as a mutagen in microbiology. Acridine yellow is similar to acridine orange, which belongs to acridine derivatives.
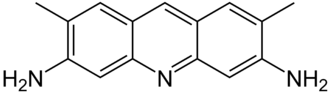 Figure 1. Chemical structure of Acridine yellow.
Figure 1. Chemical structure of Acridine yellow.
Introductions about acridine
Acridine is an organic compound and a nitrogen heterocyclic ring, and its molecular formula is C13H9N. Acridine is a substituted derivative of the parent ring. This is a planar molecule that is structurally related to anthracene and one of the central CH groups is replaced by nitrogen. Like related molecules, pyridine and quinoline, apyridine is weakly basic, which is an almost colorless solid. Commercial pyridine has no commercial application, but atidine dyes were once popular. It crystallizes in the needle.
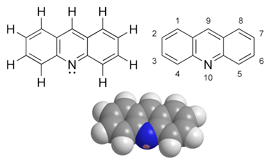 Figure 2. Acridine chemical structure.
Figure 2. Acridine chemical structure.
Applications
At one time acridine dyes were commercially significant, but they are now uncommon because they are not lightfast. Acridine dyes are prepared by condensation of 1,3-diaminobenzene derivatives. Illustrative is the reaction of 2,4-diaminotoluene with acetaldehyde:
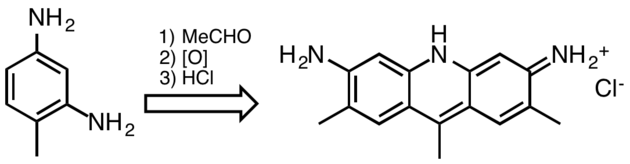 Figure 3. Synthesis of C.I. Basic Yellow 9, an acridine dye.
Figure 3. Synthesis of C.I. Basic Yellow 9, an acridine dye.
9-phenylacridine is the parent base of Chssaniline or 3,6-diamino-9-phenylacridine. It is the main component of the dye phosphine (not to be confused with phosphine gas). This dye is a by-product of making rosaniline. O-xylylenediamine forms a red salt, which dyes silk and wool to pale yellow. The salt solution is characterized by its fine yellow-green fluorescence. O. Fischer and G. Koerner synthesized phthalamide by condensing o-nitrobenzaldehyde and aniline, and reduced the resulting o-nitro-p-diaminotriphenylmethane to the corresponding o-amino compound. Oxidation to phthalamide. An isomer of acetophenone, benzoflavone, is also a dye made by K. Oehler from m-phenylenediamine and benzaldehyde. These materials condense to form tetraaminotriphenylmethane, which will lose ammonia when heated with acid, and generate 3,6-diamino-9,10-dihydrophenylacridine, which can be obtained by oxidation. It is a yellow powder that dissolves in hot water.
Reaction
The acridine shows the expected reaction of an unsaturated N-heterocycle. It undergoes N-alkylation reaction with alkyl iodide to form alkyl cripyridinium iodide. The alkyl iodide iodide is easily converted into N-alkyl apyridone by the action of basic potassium ferricyanide.
Reference:
- Maier W.; et al. Synthesis of 1,3-dihydroxy-N-methylacridone and its conversion to rutacridone by cell-free extracts of Ruta-graveolens cell cultures. Phytochemistry. 1993, 32 (3): 691–698.
Resources

- Hoechst Dyes: Definition, Structure, Mechanism and Applications
- Mastering the Spectrum: A Comprehensive Guide to Cy3 and Cy5 Dyes
- Fluorescent Probes: Definition, Structure, Types and Application
- Fluorescent Dyes: Definition, Mechanism, Types and Application
- Coumarin Dyes: Definition, Structure, Benefits, Synthesis and Uses
- Unlocking the Power of Fluorescence Imaging: A Comprehensive Guide
- Cell Imaging: Definitions, Systems, Protocols, Dyes, and Applications
- Lipid Staining: Definition, Principles, Methods, Dyes, and Uses
- Flow Cytometry: Definition, Principles, Protocols, Dyes, and Uses
- Nucleic Acid Staining: Definition, Principles, Dyes, Procedures, and Uses
Online Inquiry

